Building a Highly Available Infrastucture using Terraform
Journey: 📊 Community Builder 📊
Subject matter: Building on AWS
Task: Building a Highly Available Infrastucture using Terraform!
This project practices Automation and Reliability.
Using the 6 Pillars of the AWS Well-Architected Framework, Operational Excellence, Security, and Reliability will be achieved in this build.
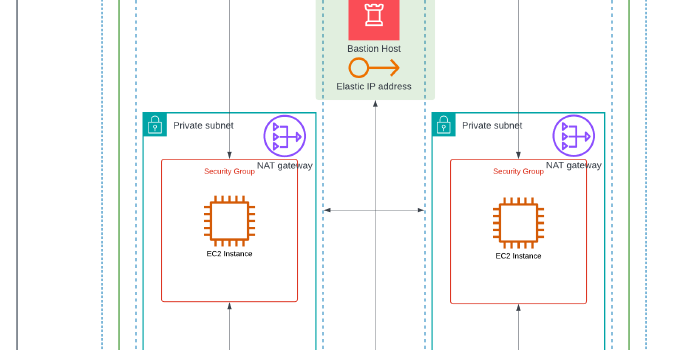
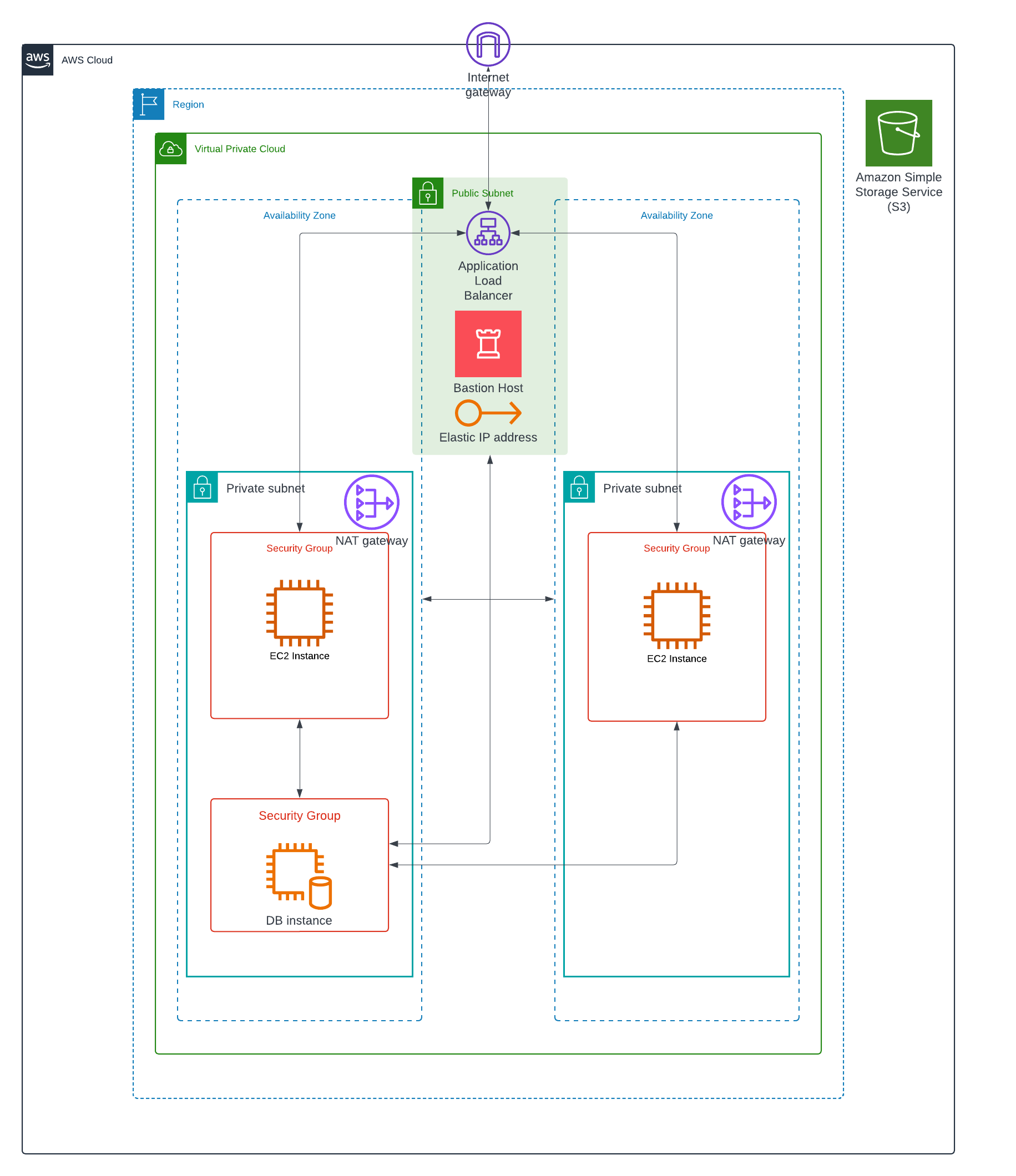
This week, I built a VPC hosting an Application Load Balancer (ALB) that balanced traffic across two EC2 Instances serving as Web servers. In the mix, there is another instance serving as a Bastion host and another instance hosting a postgres database.
Having an ALB in the environment setup ensures high availability. If we were to also add in an Auto Scaling Group, it would also increase scalability.

Resource credit: This IaC architecture was created using guidance from Christiana Shedrack on Medium Here.
What did I use to build this environment?
- Visual Studio Code platform
- Terraform
- AWS CLI
What is built?
- A single VPC
- A new EC2 Key Pair
- An S3 Bucket
- A Load Balancer (ALB)
- ALB Listeners
- ALB Target Groups
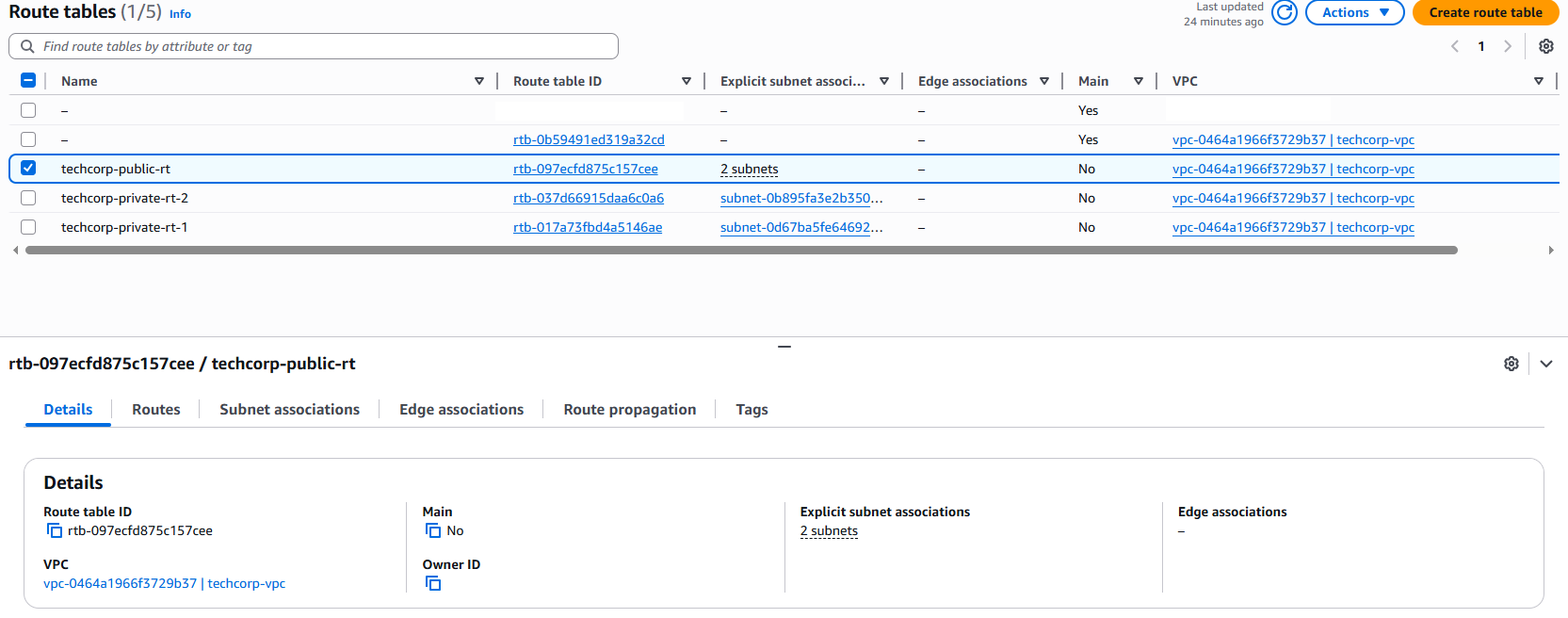
- Custom Route Tables
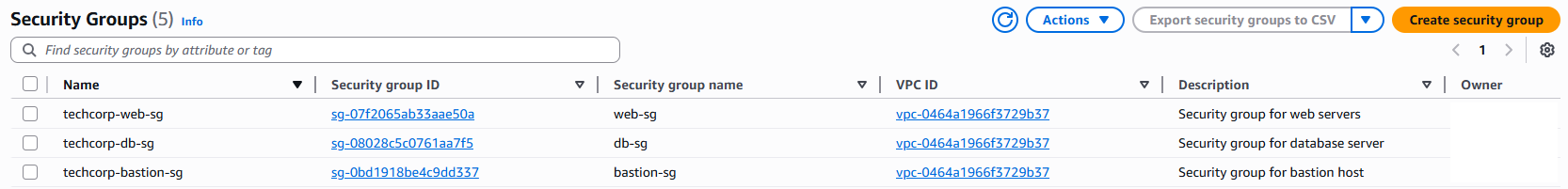
- Security Groups
- An Internet Gateway
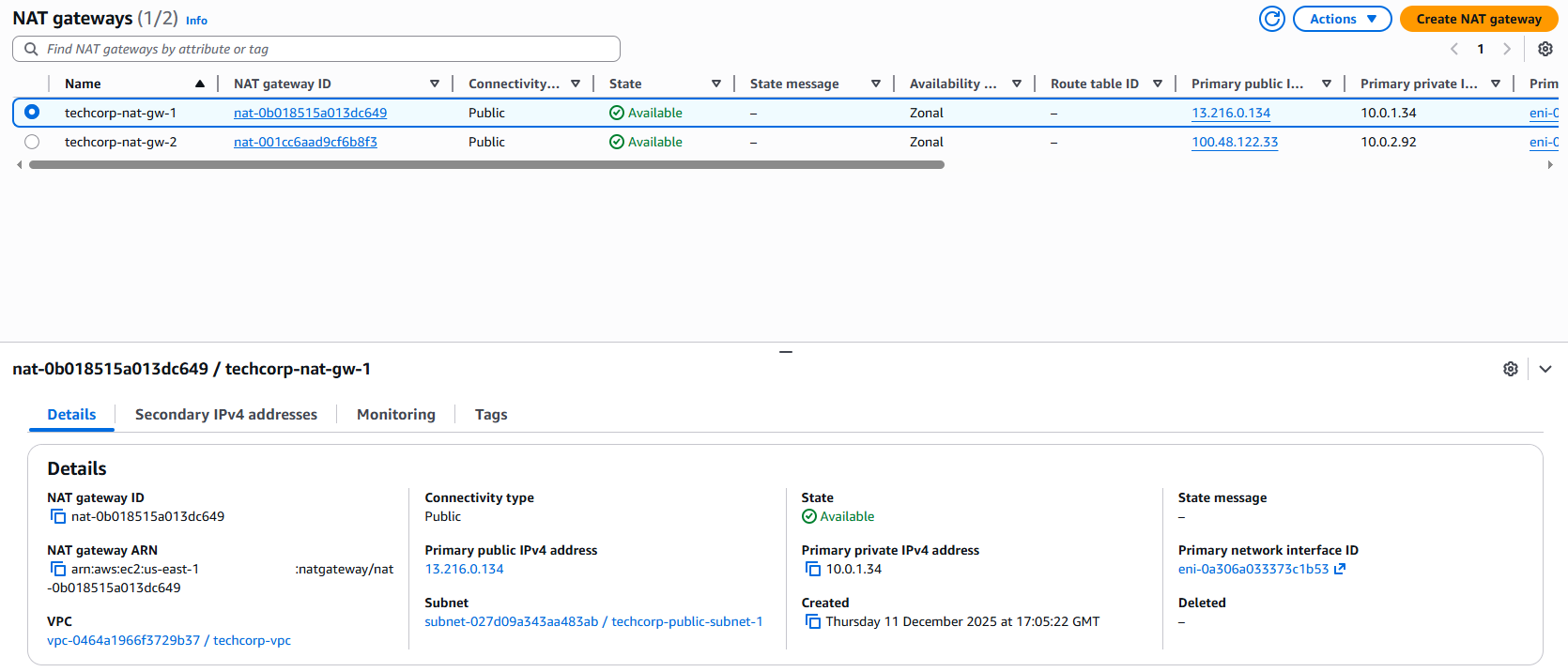
- Two NAT Gateways
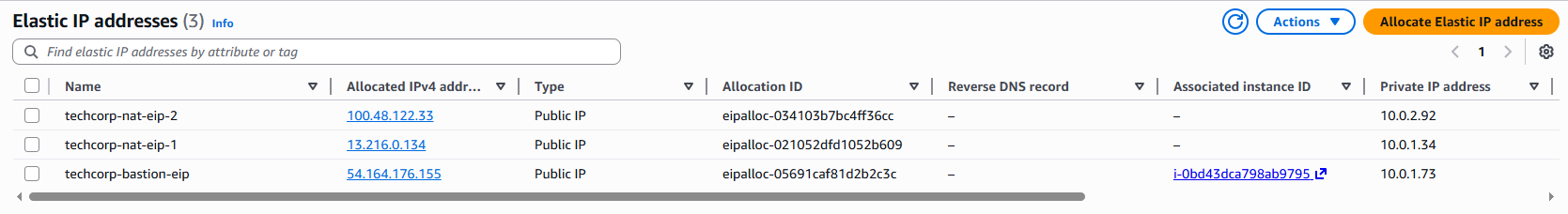
- Elastic IPs
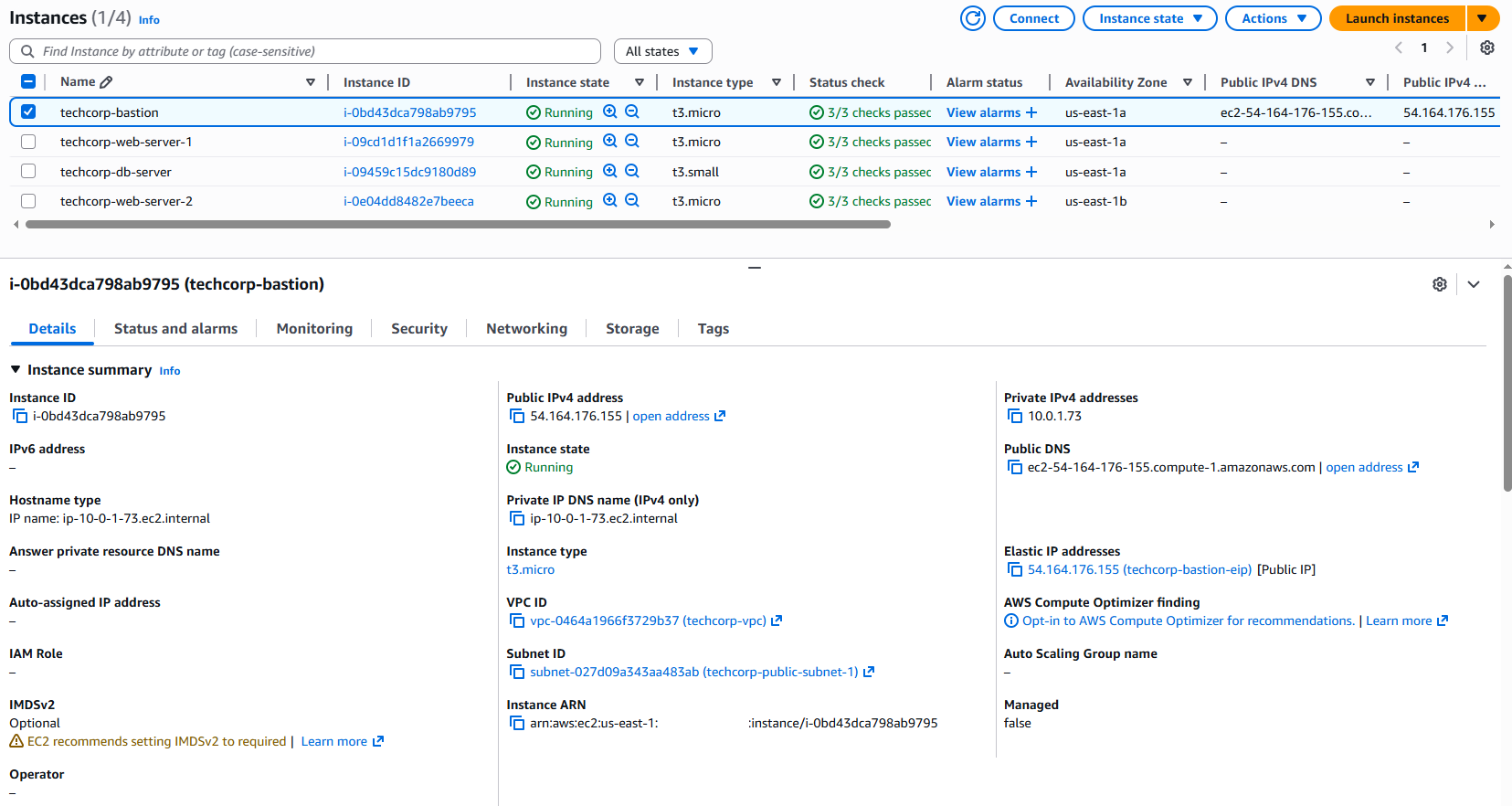
- Four EC2 instances:
- Two Web servers
- One Database server
- One Bastion server
- Two websites, one hosted on each Web server, are being load-balanced
More information on Load Balancers can be found here: https://docs.aws.amazon.com/elasticloadbalancing/latest/application/introduction.html
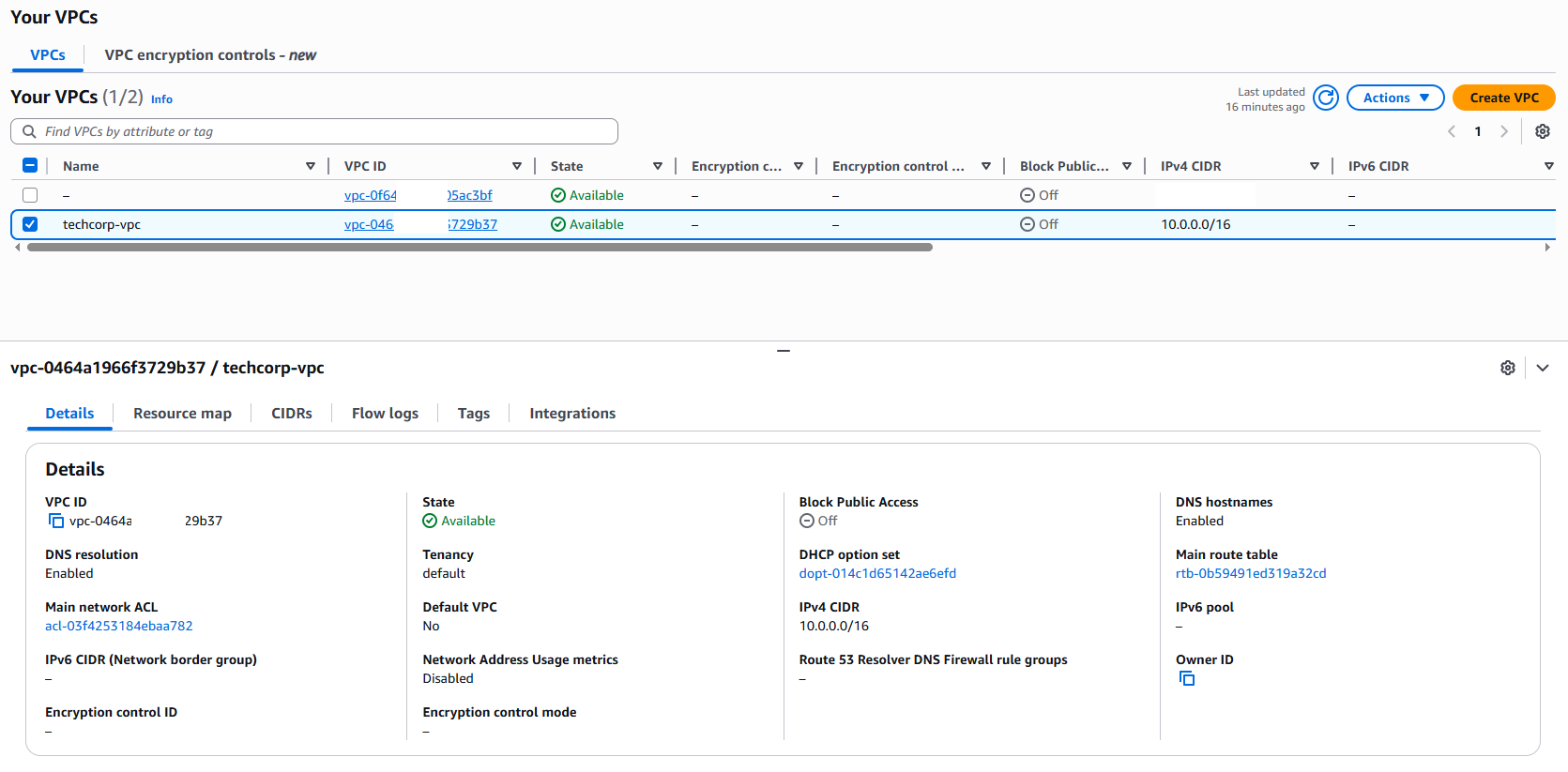
In this task, I used Terraform to create a single VPC with an S3 Bucket storing the Terraform remote state.
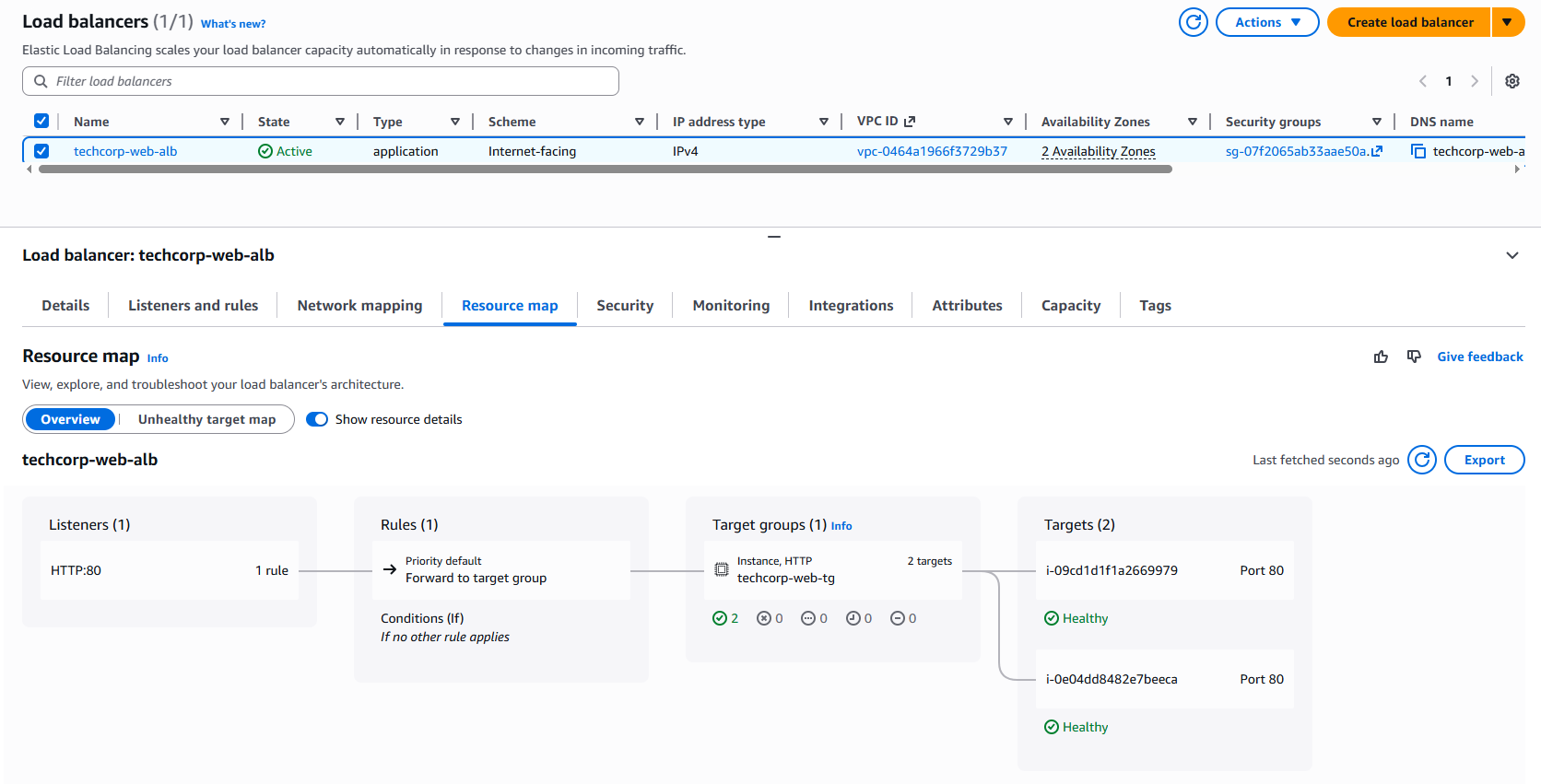
I built an Application Load Balancer to distribute application traffic evenly and then hosted one EC2 instance in each Availability Zone. I used custom Route Tables and Security Groups to protect the resources in the environment and ensured the private-facing EC2 instances had an Internet Gateway so the web elements were accessible from the public internet, via the ALB.
Each EC2 Instance had a website front end built using HTML that had custom identifiers to highlight the instance being used to serve web traffic.
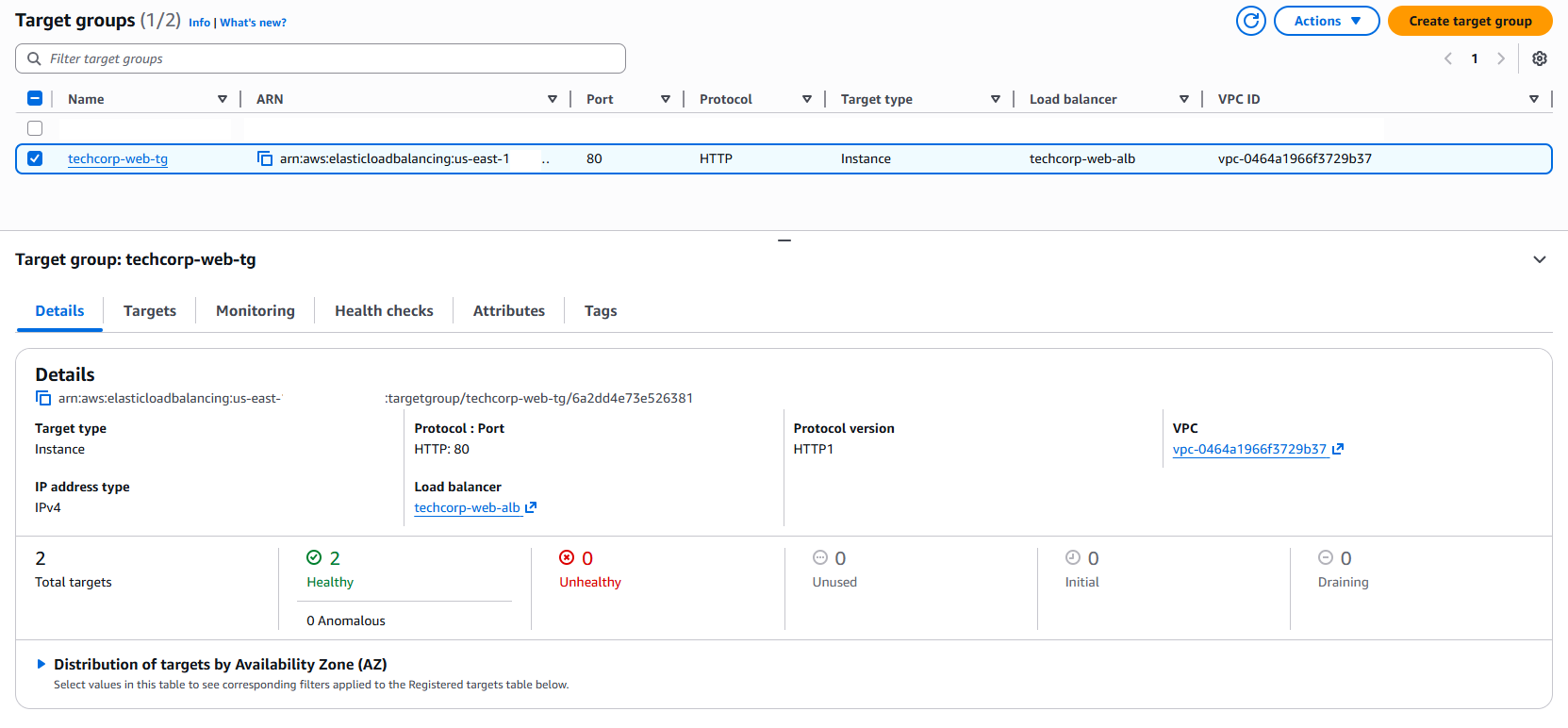
The ALB had a listener attached to listen for incoming connections on the specific port ID and also target groups to define how the ALB distributes traffic to the registered EC2 targets.
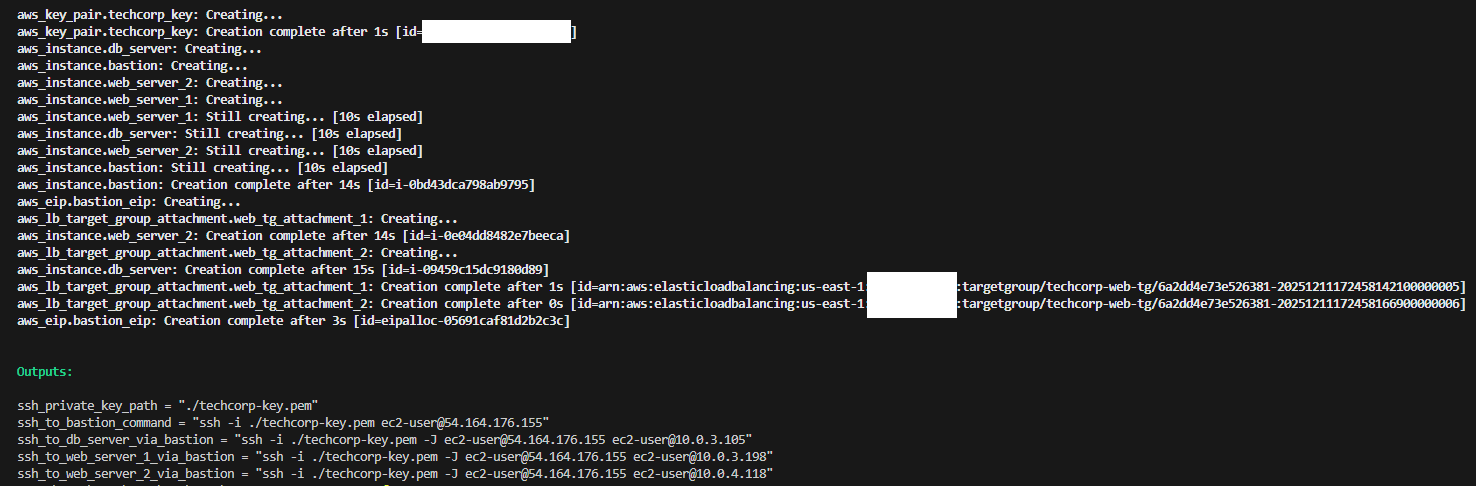
I used Terraform to deploy the entire environment and waited for it all to come online.
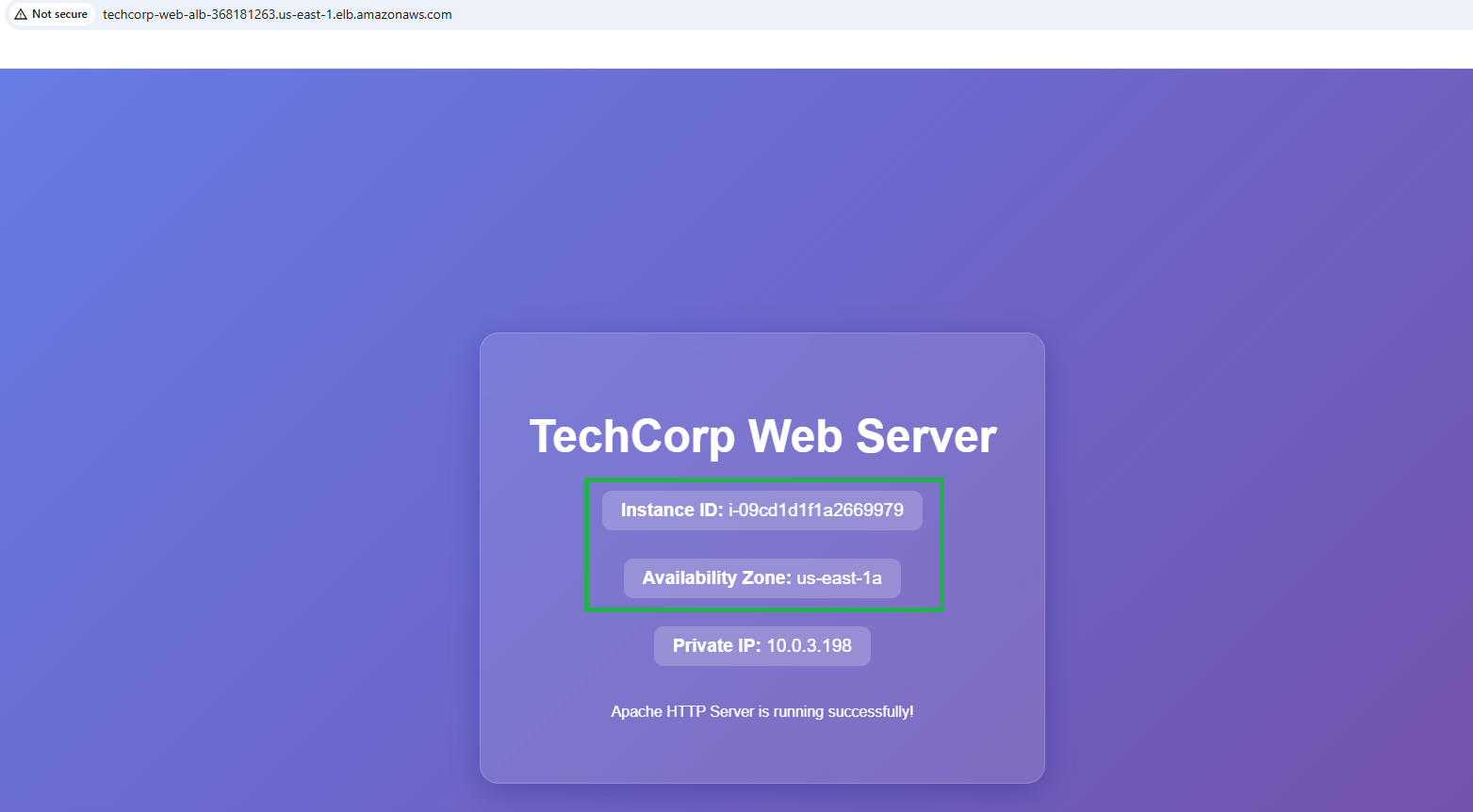
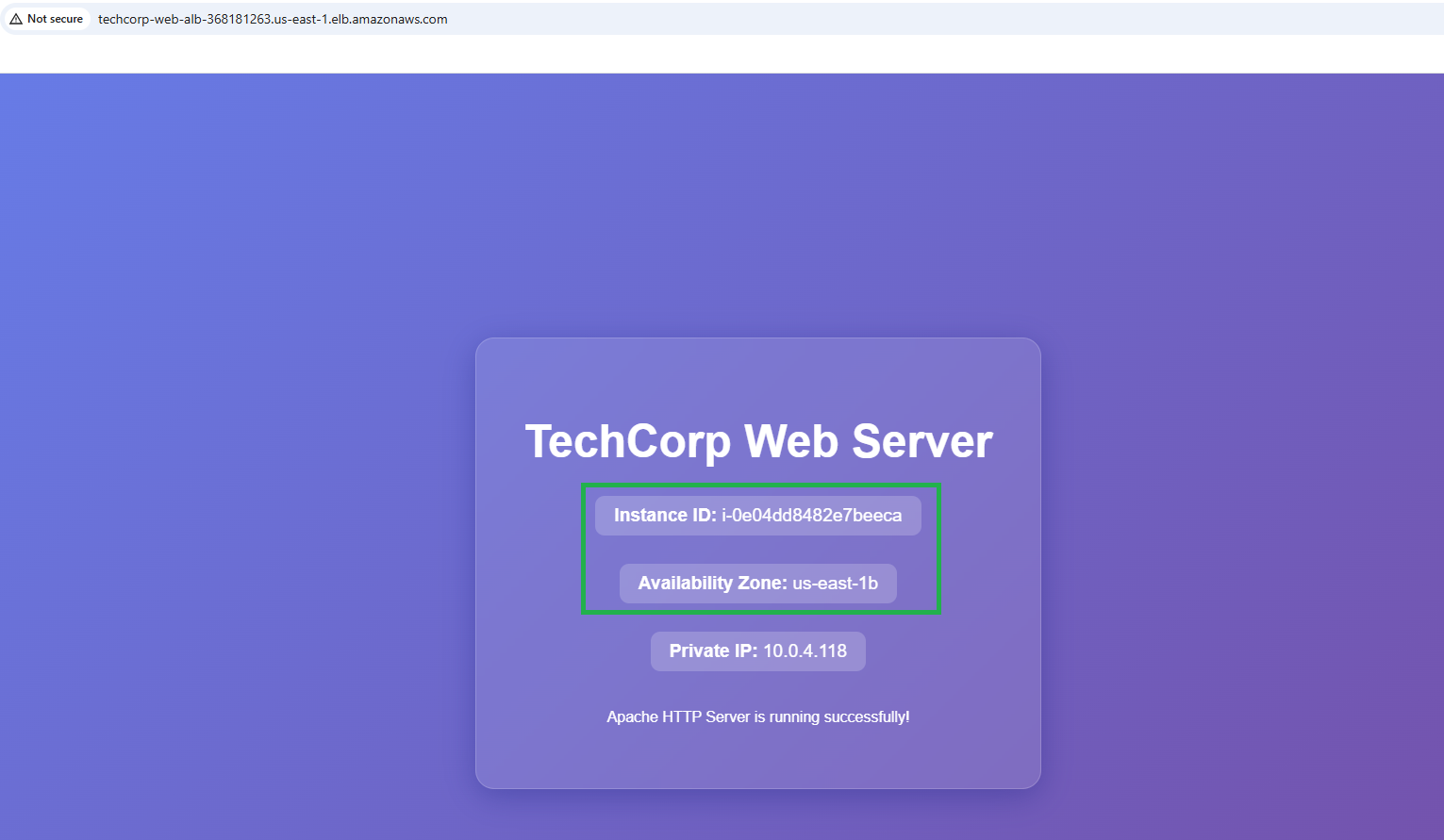
The Terraform Output identified the ALB DNS name, which I used to access the websites that had been built. Each time I refreshed the website DNS name, the ALB rerouted traffic to the other instance, demonstrating an even distribution of web traffic to serve the simple static website.

Interestingly, I ran into a problem again, which I had actually documented as a fix on my blog last year and this got me back on track again: https://www.barnybaron.com/article/20241006-ssh-connection-failing-from-windows-os/
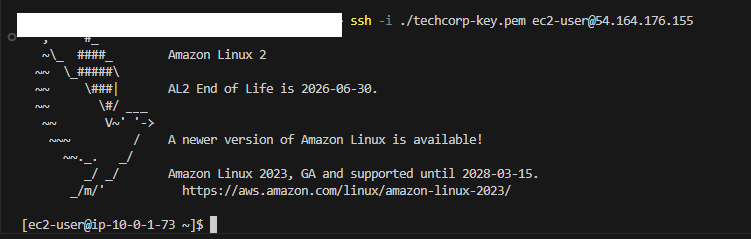
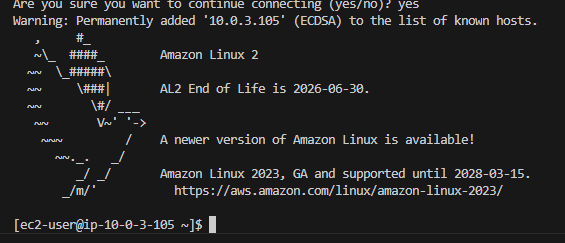
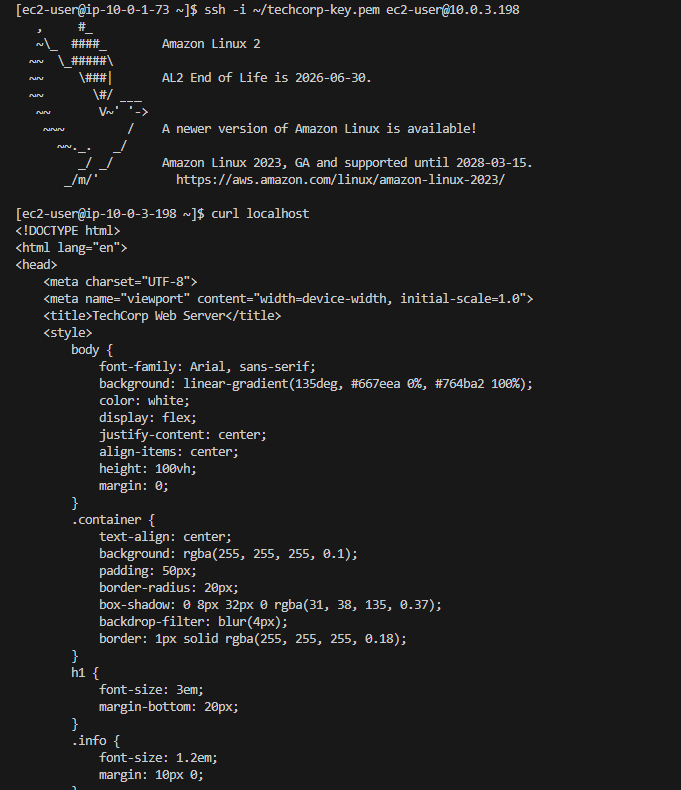
I use VScode for my deployment, and after initially testing that I could not SSH directly to my Web servers, I SSH onto my Bastion host. From there, I copied my new Key Pair private key onto the Bastion (in a .ssh dir) and was able to jump to both Web servers and also to my Postgres database server!
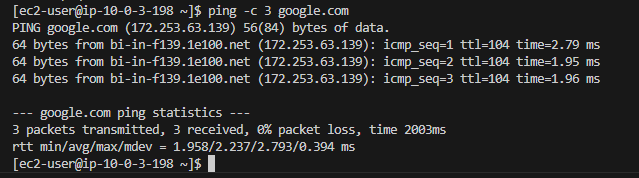
From within both Web servers, I was able to get out to the internet via the NAT Gateways sitting each Availabilty Zone. I was also able to check systemctl services and generally have a look around the directory structure.
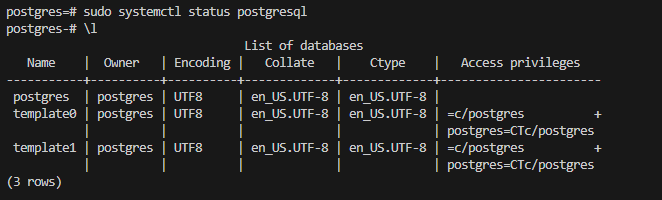
After I had completed this, I jumped onto my Postgres DB server instance from the Bastion, installed the database, checked services, and then ran some query commands.
All in all, a great lab to work from, which I would highly recommend trying out!
After documenting the lab, taking screenshots of everything, and running through various test use cases to prove the environment was secure, I then used Terraform to tear it down!
Some of the highlights…
Terraform build:
Terraform structure:
VPC built:
VPC route view:
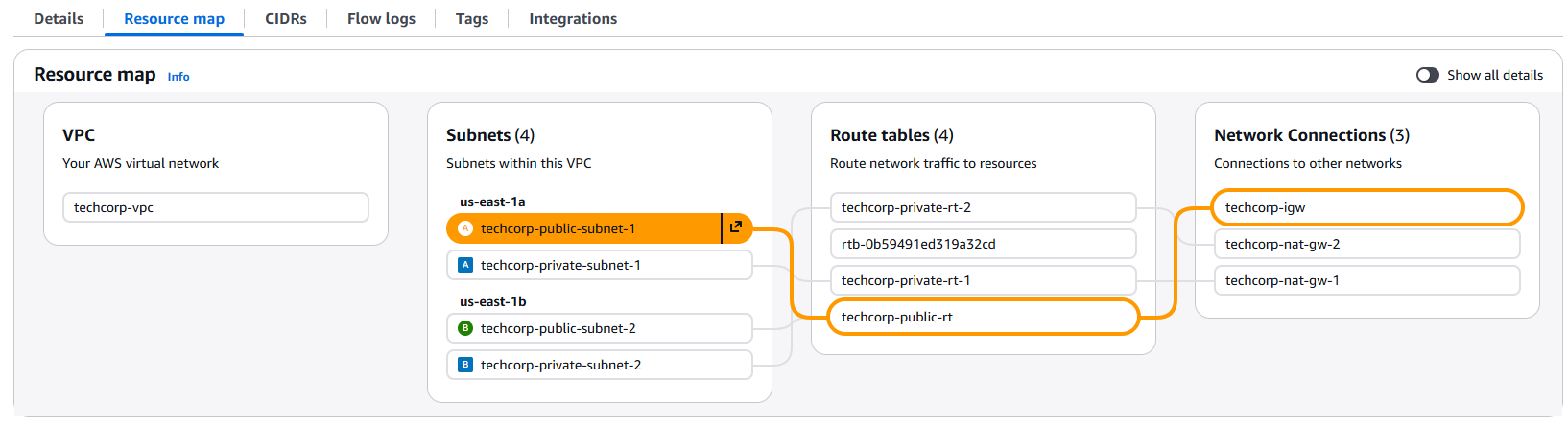
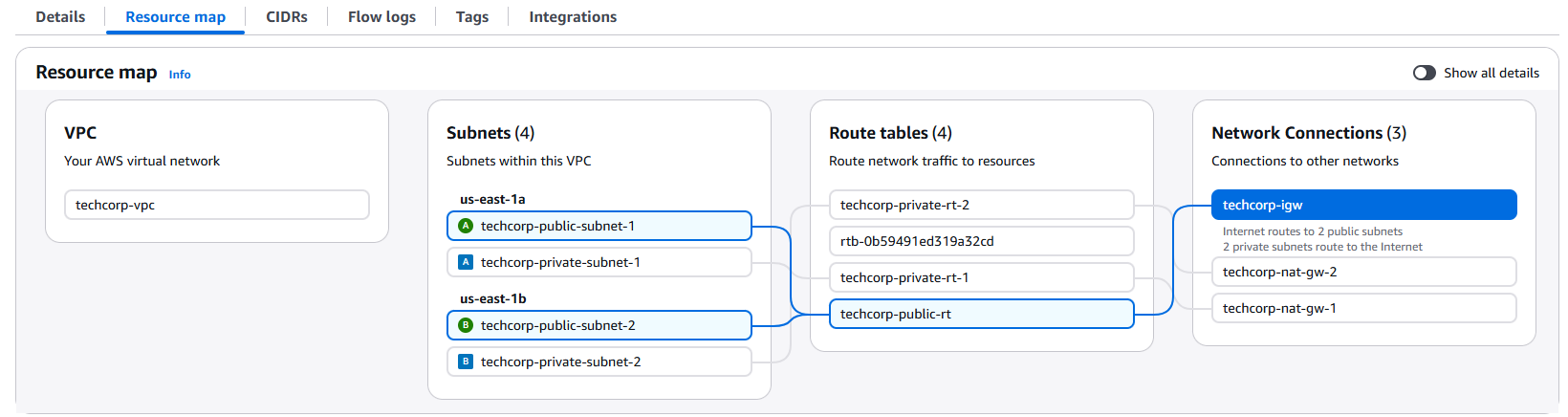
VPC route connections:
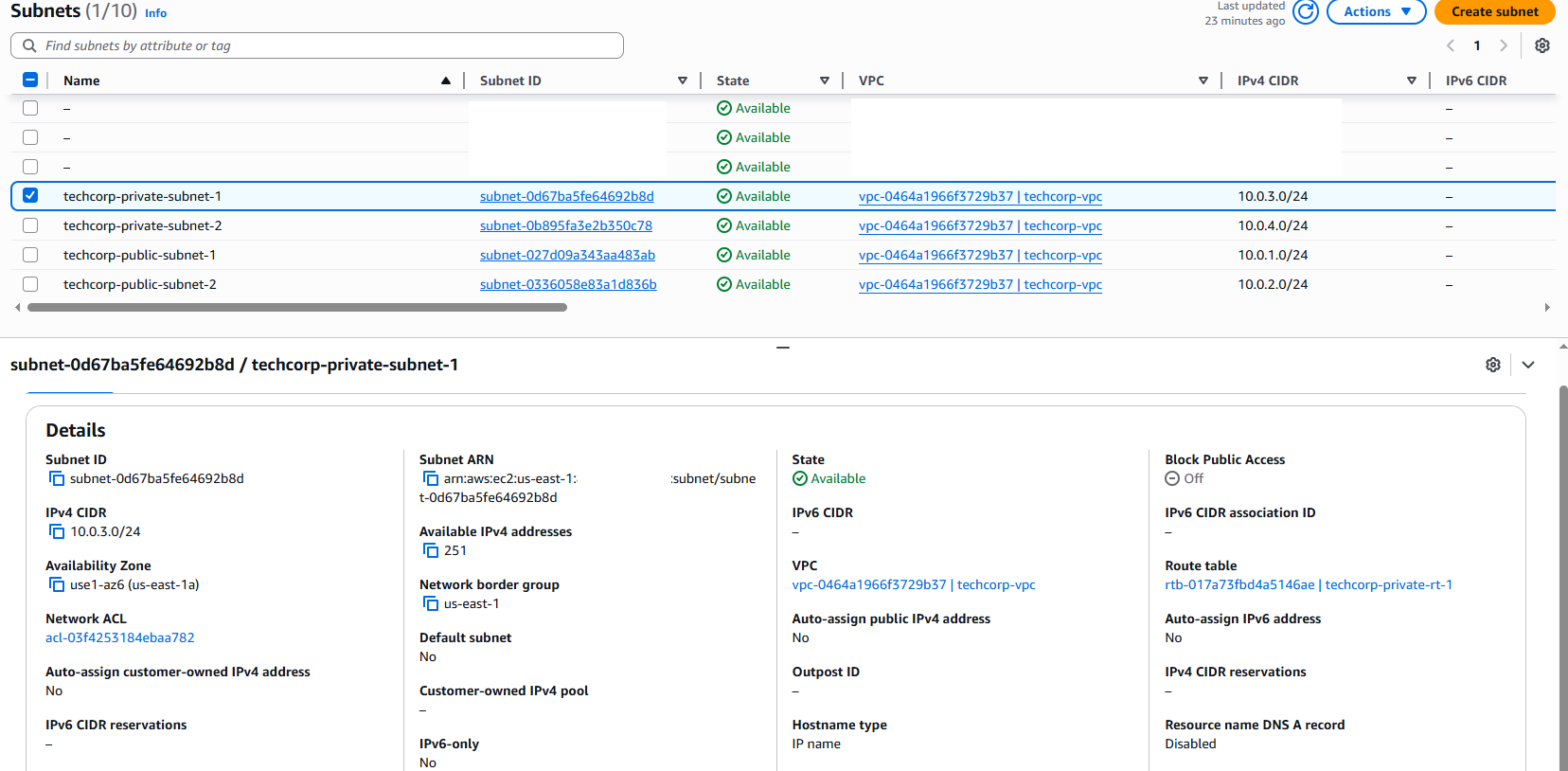
Subnets:
Resource tagging:
Route Tables:
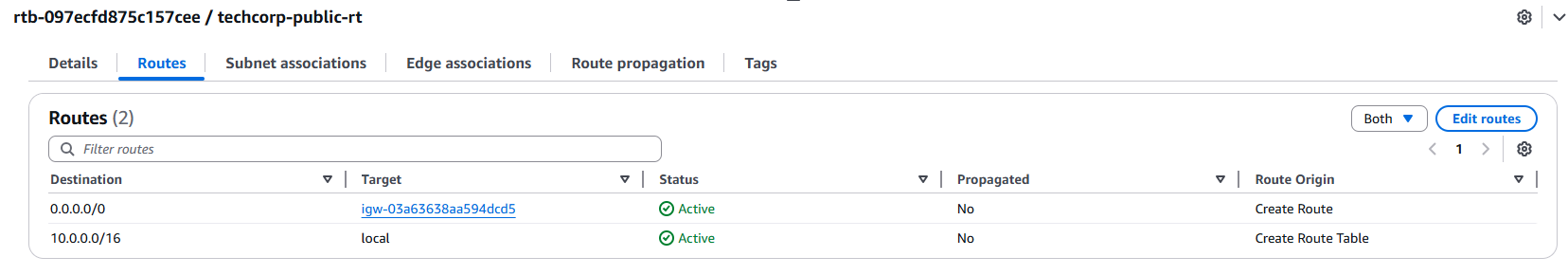
Routes:
Elastic IPs:
NAT Gateways:
Security Groups:
Instances:
ALB:
ALB Target Groups:
Load Balancer in action: Instance A
Load Balancer in action: Instance B
SSH to Bastion:
SSH to Postgres DB:
Database install:
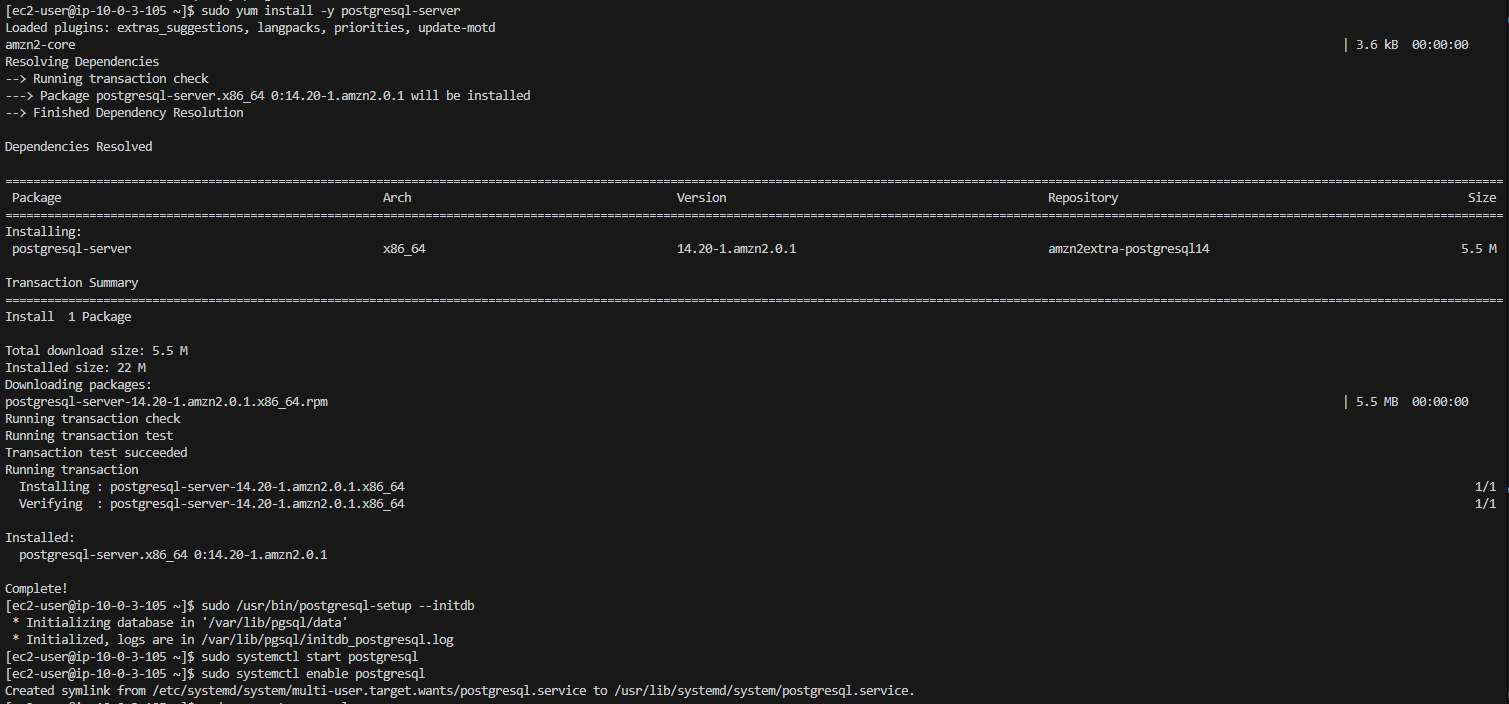
Database install:
Connection to Web Server:
Web server connecting to the internet via NAT Gateway:
Web server services:
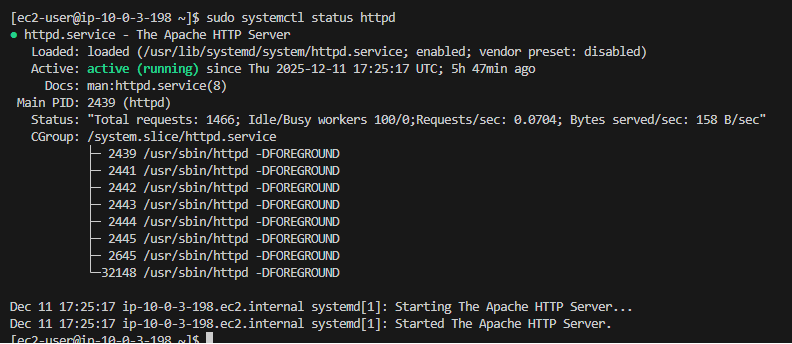
Terraform cleanup:
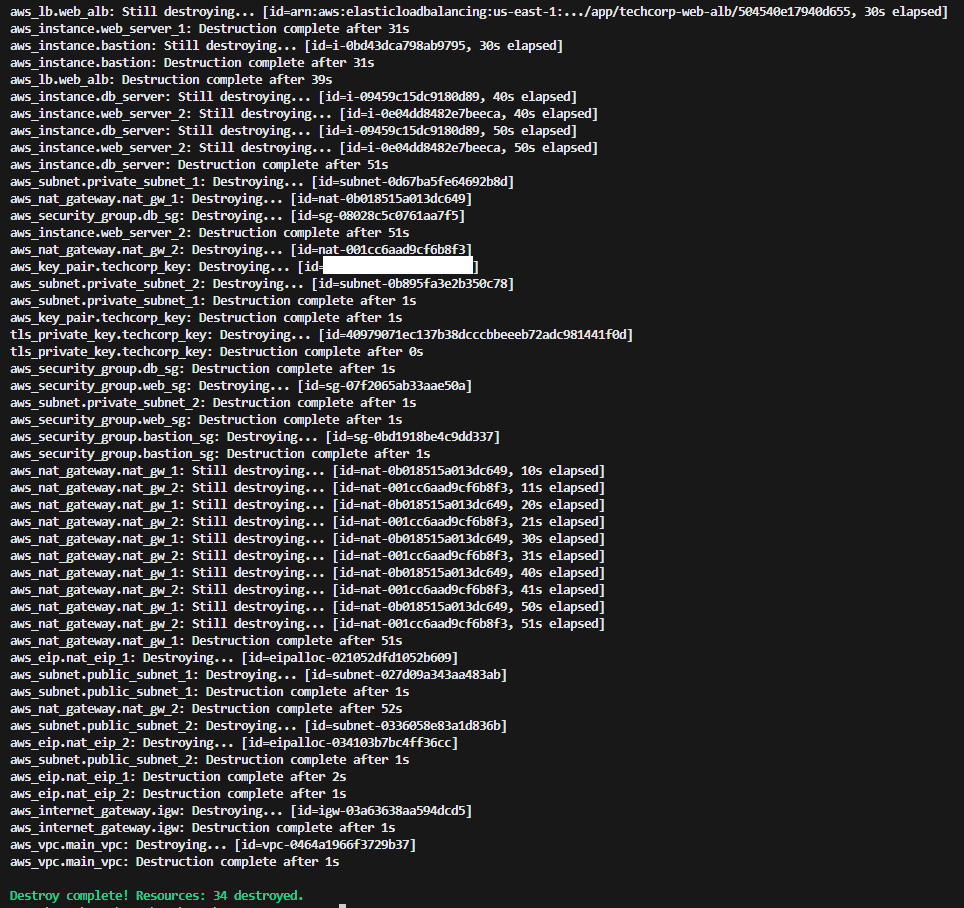
Environment teardown:
My interpretation of the architecture:
I hope you have enjoyed the article!